This post was most recently updated on February 20th, 2023.
3 min read.This article explains one possible reason why you might run into an error like “Variable reference is not valid. ‘:’ was not followed by a valid variable name character. Consider using ${} to delimit the name” when using a PowerShell task in an Azure DevOps pipeline. But hey – at least Azure DevOps is helpful enough to point out the line that causes trouble, right?
Not so fast. Confusingly, the offending line might be this:
Write-Host ('##vso[task.debug]$LASTEXITCODE: {0}' -f $LASTEXITCOD …
Not something you even have in your script, but rather part of Azure DevOps’ ceremony! But.. Azure DevOps pipelines wouldn’t mess with your code to break it, right? Surely, there’s something else going on…
So – what gives?
Problem
Let’s take a closer look at the errors you might run into.
The way Azure DevOps outputs PowerShell errors is not pretty. It might look something like the below:
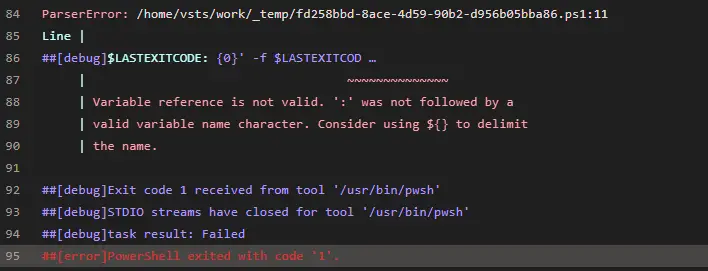
##[error]ParserError: /home/vsts/work/_temp/4954678d-6ebb-48eb-93df-b799c6c58eb4.ps1:35
Line |
35 | Write-Host ('##vso[task.debug]$LASTEXITCODE: {0}' -f $LASTEXITCOD …
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
| Variable reference is not valid. ':' was not followed by a
| valid variable name character. Consider using ${} to delimit
| the name.
And if you have system.debug enabled, your errors are going to be even worse and even more difficult to understand! Oh, and there’s going to be a LOT of them.
But what’s the actual reason?
Reason
By doing some googling, you can pretty quickly find out what this error is actually complaining about. It is a parsing error – so Azure DevOps didn’t even try to actually execute your script. It never got that far!
The error – “Variable reference is not valid. ‘:’ was not followed by a valid variable name character. Consider using ${} to delimit the name” – is mostly an internal one. Parsing fails and throws the Azure DevOps agent off before it even gets to running your stuff.
In my particular case, I was cursed by Visual Studio Code’s cool autocomplete, which added extra double quotes for me. Unfortunately, inside PowerShell tasks in YAML files, this script is not validated. Not even for syntax. So the addition went unnoticed.
Okay. But how does that help us validate the pipelines and find what the issue might be in our particular cases?
Well, read on!
Solution
The solution is to verify your script parses correctly. It’s not easy to do inside a YAML file, but there’s a workaround. Well, there’s always a workaround, isn’t there?
Let’s see how to do that easily!
Time needed: 5 minutes
How to validate PowerShell tasks in YAML files?
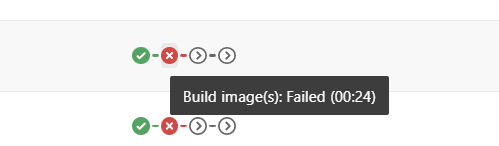
- Find the PowerShell tasks in the offending Job or Stage
You’ll need to find the PowerShell task(s) that are giving you trouble. Navigate to the failing step(s) in Azure DevOps to figure out which pipeline stage, job, and task/step you need to modify.
- Extract the PowerShell script contents
Copy-paste the script step contents from the YAML file to a new file.
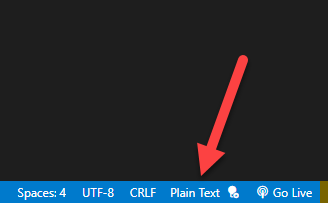
- Change the Language Mode of the file
Change the file’s “Language Mode” by clicking this in the bottom toolbar.
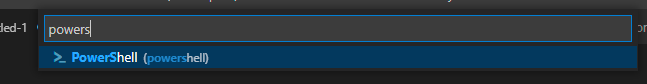
- Set the Language Mode to “PowerShell”
You can set the Language Mode as shown below:
- Observe the beautiful syntax errors!
Now you should get those useful squiggly lines below something! It might not be exactly the right place – in my example below, the first arrow shows a double quote (exactly what caused me this issue!), but the latter arrow shows where the squigglies appear.
Still, it’s an improvement! See below as to how it’ll look like: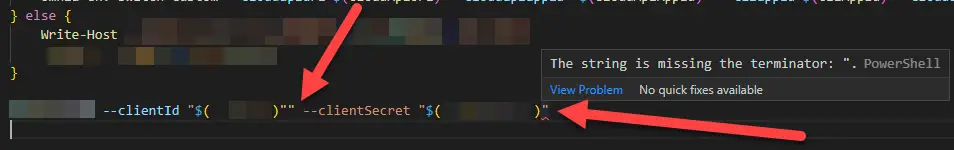
Okay, I know, I know – it’s a workaround at best. But it’ll help you fix the issue – and thoughtful workarounds are what I commonly share, so… 😅
If you find a nicer way to do this, post it in the comments section below!
- How to fix PowerToys FancyZones in Windows 11? - September 24, 2024
- How to export the whole SSL (or TLS) certificate chain based on the original using PowerShell? - September 17, 2024
- How to solve keyboard shortcuts not working in Google Chrome on Windows? - September 10, 2024

![Azure DevOps pipelines suddenly failing with "##[error]#0 building with default instance using docker driver" Azure DevOps build pipelines failing](https://www.koskila.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/image-7-125x125.png)
